Hospital readmissions are healthcare's $30 billion nightmare. Every year, one in five Medicare patients bounce back within 30 days of discharge – cycling through the same revolving door while hospitals eat CMS penalties averaging $217,000 per facility. It's not just financial disaster; these readmissions represent systematic failures in discharge planning, follow-up care, and identifying who actually needs extra attention. While administrators scramble and clinicians burn out, the same high-risk patients keep returning, each visit a missed opportunity to break the pattern.
But the interesting part is – machine learning can now predict and prevent these readmissions before they happen. Machine learning tools can actively spot the stable-looking patient who'll crash in 72 hours, flag the diabetic who'll skip follow-ups, and identify the heart failure patient whose home situation makes medication compliance impossible. This is much like giving healthcare teams superpowers. The ability to know which patients need that extra call, that home visit, that modified discharge plan. The difference between hoping patients stay healthy and knowing who needs help before they crash.
Let’s learn more about how artificial intelligence and machine learning can help reduce readmission rates in hospitals, clinics, and overall healthcare systems.
What Is Predictive Analytics in Healthcare?
Predictive analytics in healthcare is essentially a crystal ball that actually works - using data patterns to forecast what's likely to happen to patients before it happens. Instead of reacting when someone shows up in the ER, hospitals can anticipate problems while there's still time to intervene. Think of it as the difference between waiting for your car to break down versus knowing the engine's about to fail because you noticed subtle warning signs.
Traditional healthcare runs on a reactive mode: patient gets sick, patient seeks treatment, repeat. Predictive analytics flips this entirely. It spots the COPD patient whose breathing patterns suggest an exacerbation brewing three days out. It knows which diabetic will likely skip their endocrinologist appointment based on past behavior patterns, weather, and transportation issues.
Here's where machine learning leaves old-school statistics in the dust. Traditional models choke on real-world healthcare data – thousands of variables, missing information, complex interactions between conditions. They assume neat, linear relationships that rarely exist in human biology. ML thrives on this chaos. It handles massive datasets from EHRs, finds patterns humans would never spot, and understands that the relationship between blood pressure, kidney function, and readmission risk isn't a straight line. It recognizes that a 70-year-old's slightly elevated white cell count means something different than a 30-year-old's. That's not just smart mathematics – that's understanding healthcare's beautiful, messy complexity.
Role of Machine Learning in Reducing Readmission Rates
The Data Feast That Feeds Prediction
Machine learning models treat readmission prediction like a massive puzzle where every piece matters. They consume data most systems ignore: not just age and diagnosis, but ZIP code (proxy for social determinants), pharmacy refill patterns (actual medication adherence versus claimed), number of ER visits last year (healthcare utilization patterns), and even day of discharge (Friday discharges have higher readmission rates – who knew?).
The model considers obvious clinical factors – comorbidities, lab results trending wrong direction, length of stay – but also subtle social signals. Lives alone? Higher risk. Three medications changed during admission? Red flag. Previous hospitalizations at different facilities? Pattern of fragmented care. It even factors in seemingly random details like distance from the hospital and the primary language spoken. Because that elderly Mandarin speaker living 40 miles away with newly diagnosed heart failure? They're statistically way more likely to bounce back than the English-speaking retired nurse living near the hospital.
How the Magic Actually Works
Forget complex math explanations – here's what matters: classification models sort patients into buckets. High readmission risk or low risk within 30 days. The model trains on thousands of previous patients, learning patterns humans miss. It discovers that specific lab value combinations, when mixed with certain demographics and discharge destinations, spell trouble. That heart failure patient with borderline kidney function going home alone? 73% readmission probability. Same patient going to skilled nursing? 31% probability.
From Prediction to Prevention
The real power isn't predicting readmissions – it's preventing them. When ML flags high-risk patients, clinicians get specific, actionable intelligence. That 73% risk patient doesn't just get standard discharge instructions. They get daily phone check-ins for the first week, automatic home health referral, simplified medication regimen, and an appointment with cardiology within 72 hours instead of two weeks. The pharmacist gets alerted about potential adherence issues. Social work arranges transportation proactively.
The model doesn't just say "high risk" – it explains why. Medication complexity? Simplify regimen. Social isolation? Activate community support. Previous missed appointments? Schedule during preferred times with reminder calls. It's a personalized intervention based on specific risk factors, not one-size-fits-all protocols that miss half the problems.
Key Benefits of ML-Powered Predictive Analytics
Clinical Impact: Catching Problems Before They Explode
Early intervention changes everything. When ML flags a patient trending toward readmission, clinicians intervene while problems are still manageable. That subtle weight gain in heart failure patients gets addressed before it becomes full-blown pulmonary edema. Medication non-compliance gets caught on day three, not after the patient crashes. Targeted care replaces shotgun approaches – high-risk patients get intensive resources while low-risk ones aren't smothered with unnecessary interventions. Result? 30-40% reduction in preventable readmissions, fewer complications, and patients who actually recover instead of revolving through the system.
Operational Impact: Finally, Breathing Room
Staff stop drowning in crisis management. Instead of scrambling when readmissions flood the ER, teams proactively manage high-risk patients. Bed management becomes predictable – knowing who's likely to return means better capacity planning. Case managers focus on patients who actually need intensive support rather than spreading themselves thin across everyone. The chaos-to-coordination shift is dramatic.
Financial Impact: The ROI That Makes CFOs Smile
Avoiding one readmission saves $15,000 on average. Dodge CMS penalties (up to 3% of Medicare payments), and we're talking millions. Value-based care contracts suddenly become profitable when you're preventing readmissions rather than eating the costs. Insurance companies notice, offering better rates to hospitals demonstrating predictive capability. It's not cost-cutting – it's intelligent resource allocation that happens to save fortune.
Patient Experience: Actually Feeling Cared For
Patients notice when hospitals remember them. That follow-up call checking on recovery, the simplified medication schedule, the transportation arranged for appointments – it feels like actual care, not bureaucracy. Trust builds when patients realize their healthcare team anticipated and prevented problems. They're partners in recovery, not just discharge statistics.
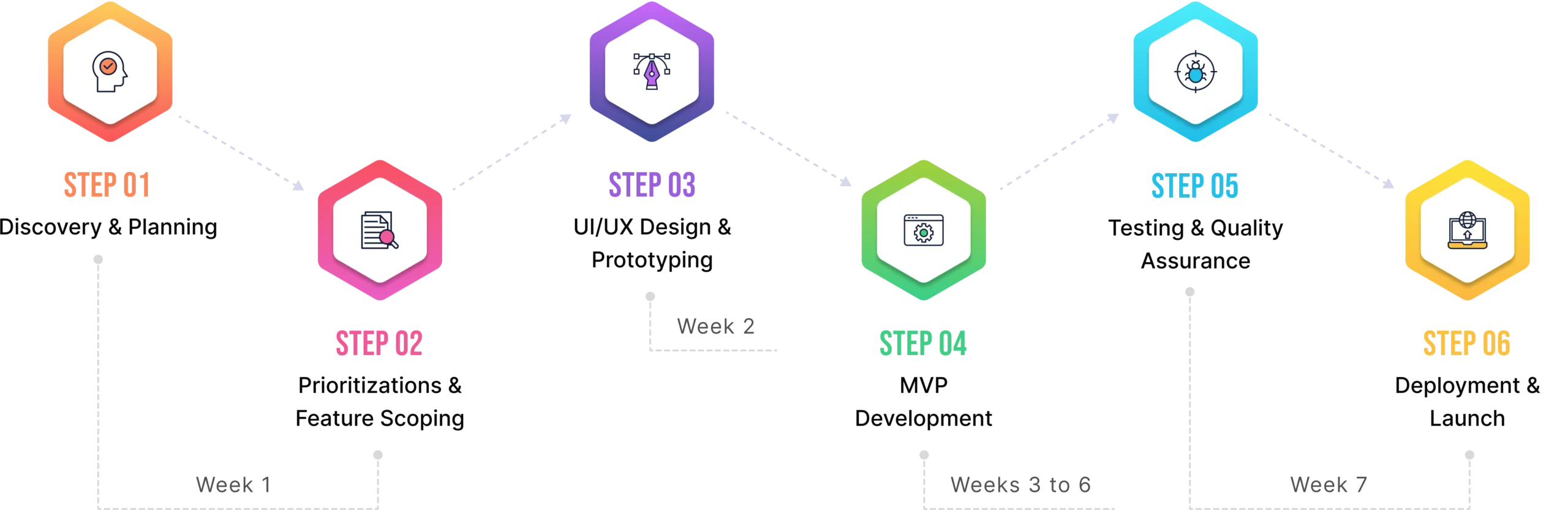
Implementation Framework: How to Deploy Predictive Analytics for Readmissions
Step 1: Define Your Problem (Specifically, Not Generally)
"Reduce readmissions" isn't a plan – it's a wish. Get surgical: Which patients keep coming back? Heart failure patients within 30 days? Diabetics with complications? Post-surgical infections? Data tells the story – pull your readmission reports and find the expensive patterns. That's your starting point. One hospital discovered 60% of readmissions came from just three conditions. Guess where they focused?
Step 2: Data Collection Without Drowning
Your EHR contains gold buried in garbage. Start with the basics: demographics, diagnoses, labs, medications. Add claims data for the full picture – it catches readmissions to other hospitals you'd miss otherwise. Layer in social determinants if possible. Wearables data? Great if you have it, not essential to start. Quality beats quantity – clean, consistent data from three sources beats messy data from ten.
Step 3: Build vs. Buy (The Eternal Debate)
Off-the-shelf models from Epic or Cerner work fine for standard cases. But if your population is unique (rural, specific ethnicities, unusual payer mix), custom models perform better. Start with vendor solutions to prove value, then customize based on what you learn. Building from scratch sounds sexy but usually means reinventing wheels that already roll perfectly.
Step 4: Integration That Actually Works
Nobody uses separate dashboards. Embed predictions directly into clinical workflow – risk scores in discharge summaries, alerts in nursing stations, flags in case management systems. One click, not five. Visible, not buried. Actionable, not academic.
Step 5: Training That Sticks
Clinicians need to understand what scores mean, not how algorithms work. "Red means schedule follow-up within 48 hours" beats explaining random forests. Use real cases from your hospital. Show success stories. Make champions of early adopters who'll convince skeptics.
Step 6: Monitor, Adjust, Repeat
Track everything: readmission rates, model accuracy, intervention compliance, staff usage. Monthly reviews catch model drift early. When performance drops, retrain with recent data. It's not set-and-forget – it's continuous evolution.
Challenges & How to Overcome Them
Data Quality: Garbage In, Expensive Mistakes Out
Your ML model is only as smart as the data feeding it. Missing lab values, inconsistent coding, duplicate records – these aren't minor annoyances, they're prediction killers. One hospital discovered their model was failing because nurses entered blood pressure in three different fields depending on shift. The fix isn't sexy but it's essential: data governance before deployment. Standardize entry fields, mandate required data points, automated cleaning protocols. Yes, it's tedious. Yes, it delays launch. But models trained on clean data achieve 85% accuracy versus 60% on messy data. That 25% difference? That's lives and millions of dollars.
Bias & Fairness: When Algorithms Discriminate
Here's the uncomfortable truth – ML models can be racist without trying. Train on historical data where minorities received less follow-up care, and your model learns that pattern. Suddenly you're flagging wealthy patients for intervention while missing high-risk minority patients. The solution requires deliberate action: audit predictions by demographics, use fairness constraints during training, include social determinants thoughtfully (ZIP code matters, but don't penalize poverty). One health system discovered their model under-predicted risk for Spanish-speaking patients by 30%. After retraining with balanced data and fairness constraints, accuracy equalized across all populations.
Regulatory Compliance: The Rules Keep Changing
HIPAA was complex enough before AI entered healthcare. Now add algorithm transparency requirements, GDPR if you have international patients, FDA guidelines for clinical decision support. The key? Build compliance into architecture, not bolt it on later. Audit trails for every prediction, explainable models that show their work, data governance that satisfies regulators. Partner with legal early – they're annoying but essential.
Trust & Adoption: Winning Hearts and Minds
Clinicians trust their gut, not black boxes. Explainable AI isn't optional – it's mandatory for adoption. Show why patients are flagged: "High risk due to: previous readmission + lives alone + 5+ medications." Let clinicians override predictions with documented reasoning. Share accuracy metrics transparently, including where models fail. When doctors see models catching patients they might've missed, skepticism becomes advocacy
Future Outlook: The Evolution of Predictive Analytics in Healthcare
The Data Revolution That's Actually Revolutionary
Five years from now, today's predictive models will look like flip phones. Multimodal data integration is transforming predictions from educated guesses to near-certainty. Your smartwatch detecting irregular heartbeats, continuous glucose monitors streaming real-time data, genomic profiles revealing medication metabolism rates – all feeding models that update predictions hourly, not monthly. One pilot program combining wearable data with traditional EHR information improved readmission prediction accuracy from 76% to 91%. Imaging data adds another dimension – chest X-rays revealing subtle patterns predicting respiratory failure days before symptoms appear. This isn't data overload; it's finally having the complete picture.

Deep Learning: When Models Get Scary Smart
Current models are like medical students – competent but limited. Deep learning models are becoming attending physicians. They're discovering risk patterns humans never imagined: the combination of specific voice pattern changes, gait alterations from phone accelerometers, and prescription refill timing that predicts falls in elderly patients with 94% accuracy. Real-time prediction is the game-changer. Instead of daily risk scores, imagine continuous monitoring where alerts fire the moment risk escalates. Patient's heart rate variability suddenly changes? Model notices. Activity levels drop unexpectedly? Flag raised. It's shifting from periodic check-ins to constant guardian angel mode.
Value-Based Care: Where Prediction Becomes Profit
The financial model of healthcare is flipping. Hospitals paid for keeping people healthy, not treating sickness. Predictive analytics makes this sustainable. Insurance companies are already offering premium contracts to hospitals demonstrating predictive capabilities. Why? Because preventing one readmission costs $500 in interventions but saves $15,000 in treatment. Medicare Advantage programs using advanced predictive analytics report 20-30% better margins while improving patient outcomes. The organizations investing in predictive analytics today aren't just improving care – they're positioning themselves as winners in tomorrow's value-based ecosystem where prediction equals profit and prevention pays dividends.
Final Thoughts
Predictive analytics for readmission reduction is happening right now in hospitals that have grown tired of watching the same patients bounce back month after month. The technology works, the ROI is proven, and the clinical outcomes speak for themselves. However, implementing predictive analytics isn't about buying fancy software or hiring data scientists. It's crucially important to fundamentally change how healthcare operates – from reactive firefighting to proactive prevention. The tools exist, the evidence is overwhelming, and patients deserve better than our current revolving-door system. The only thing missing is the decision to act.