Over 90% of hospitals in the U.S. have adopted EHR systems, yet integration remains one of healthcare's biggest headaches. Providers spend thousands per physician on implementation, only to discover their new system doesn't connect with existing lab software, billing platforms, or telemedicine apps. The result? Staff waste hours on manual data entry, critical information gets siloed, and patient care suffers.
EHR integration is about making all your healthcare systems share information automatically—no duplicate records, no missed allergies, no workflow disruptions. This blog shows you exactly how to integrate EHRs successfully. You'll learn proven best practices, common challenges every provider faces, and practical solutions that actually work. Whether you're connecting your first system or fixing existing integration issues, we'll help you build a truly connected healthcare ecosystem.
1. Why EHR Integration Matters
Let's cut to the chase—EHR integration isn't just another IT project to check off your list. It's the backbone of modern healthcare delivery. When your systems actually talk to each other, everything changes.

Better Patient Care, Better Outcomes
Integrated EHRs mean your cardiologist sees the medications your primary care doctor prescribed yesterday. The ER knows about that penicillin allergy documented three years ago. Lab results flow directly into patient charts without anyone hitting "copy-paste." This isn't just convenient—it prevents medical errors that affect 1 in 10 patients. When providers have complete, real-time information, they make better decisions. Period.
Data at Your Fingertips
Remember hunting through three different systems to find one patient's complete history? Integration ends that. All data lives in one accessible place. Doctors spend less time clicking and more time with patients. Nurses pull up records in seconds, not minutes. The entire care team works from the same playbook, updated in real-time.
Workflows That Actually Work
Here's what proper integration kills: duplicate data entry, paper forms, phone tag between departments, and those endless "let me check another system" moments. Administrative tasks that took hours now take minutes. Staff stop fighting technology and start using it. One mid-size clinic we worked with cut documentation time by 40% just by integrating their EHR with their scheduling and billing systems.
The New Reality: Everything's Connected
Healthcare isn't slowing down. Telemedicine platforms need patient histories. AI diagnostic tools need lab data to spot patterns. IoT devices like continuous glucose monitors and smart blood pressure cuffs generate thousands of data points daily. Without integration, all this innovation is worthless.
The demand for seamless integration is exploding. Hospitals using integrated EHRs report 23% higher patient satisfaction scores and 18% reduction in readmission rates. Meanwhile, those still using disconnected systems are losing patients to competitors who've figured this out.
The healthcare providers winning today aren't necessarily the biggest or most advanced. They're the ones whose systems work together seamlessly, delivering better care without the friction. That's what integration delivers—and why it's not optional anymore.
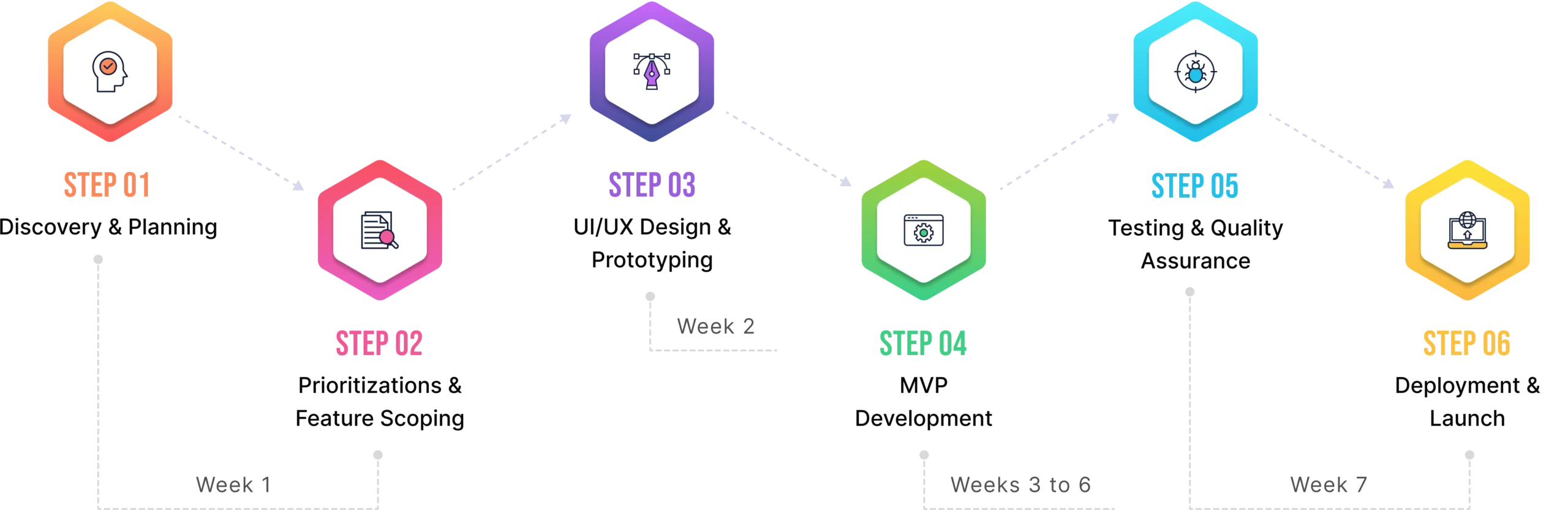
2. Best Practices for EHR Integration
Integration done right saves money and headaches. Done wrong, it's a million-dollar mistake. Here are the practices that separate smooth implementations from total disasters.

A. Conduct a Comprehensive Needs Assessment
Before touching any technology, figure out what you actually need. What are your organizational goals—reducing wait times? Improving billing accuracy? Expanding telehealth? Map these goals to specific requirements.
Then audit your existing systems. That scheduling software from 2015? The billing platform you love? Does the lab system that works perfectly? List everything, including the ancient fax machine (yes, it counts). Document current workflows—how patient data moves from registration to discharge. You'll spot bottlenecks and redundancies that integration can fix.
B. Choose the Right EHR System
Not all EHRs are created equal. Look beyond flashy demos and focus on what matters. Can it scale when you grow from 10 to 50 providers? Does the vendor have a solid track record, or will they vanish in two years? Are they HIPAA-compliant out of the box, or will you need expensive add-ons?
Here's the non-negotiable: insist on interoperability standards. HL7 and FHIR aren't just acronyms to impress people—they're the languages that let systems communicate. Without them, you're building another silo. Ask vendors point-blank: "Does this support FHIR APIs?" If they hesitate, walk away.
C. Plan for Data Migration
Moving patient data is like moving houses—except you can't lose a single sock. Start with data cleaning. Remove duplicates, fix formatting issues, standardize naming conventions. Messy data in means messy data out.
Use proven migration tools that maintain data integrity. Set up validation checkpoints—compare random samples between old and new systems. Run parallel systems temporarily to catch issues before going fully live. And always, always keep backups of everything.
D. Ensure Stakeholder Engagement
The fastest way to fail? Surprise your staff with a new system on Monday morning. Instead, involve everyone early. Clinicians need workflows that match how they actually work. IT needs to understand technical requirements. Administrators need to see ROI.
Create a diverse implementation team. Run regular demos. Listen to complaints—that "minor" issue nurses mention could derail everything. Provide real training, not just login credentials and a PDF manual. When people feel heard and prepared, adoption rates soar.
E. Prioritize Security and Compliance
One breach can cost millions and destroy trust forever. Build security in from day one. Encrypt data in transit and at rest. Implement role-based access controls—receptionists don't need access to psychiatric notes.
Stay compliant with HIPAA, GDPR, and state regulations. Document everything. Run regular security audits. Yes, it's tedious. But it's far less tedious than explaining to patients why their data is on the dark web.
F. Test and Iterate
Never go live systemwide immediately. Start with one department or a handful of providers. Run pilot tests for 2-4 weeks. Gather feedback obsessively. Fix issues while the impact is small.
Post-integration isn't "set and forget." Healthcare changes, regulations update, user needs evolve. Plan quarterly reviews. Keep improving. The best integrations are living systems that get better over time.
3. Common Challenges in EHR Integration
Let's talk about what goes wrong—because it will go wrong. Every integration hits these roadblocks. The difference between success and failure is knowing they're coming and having a plan.
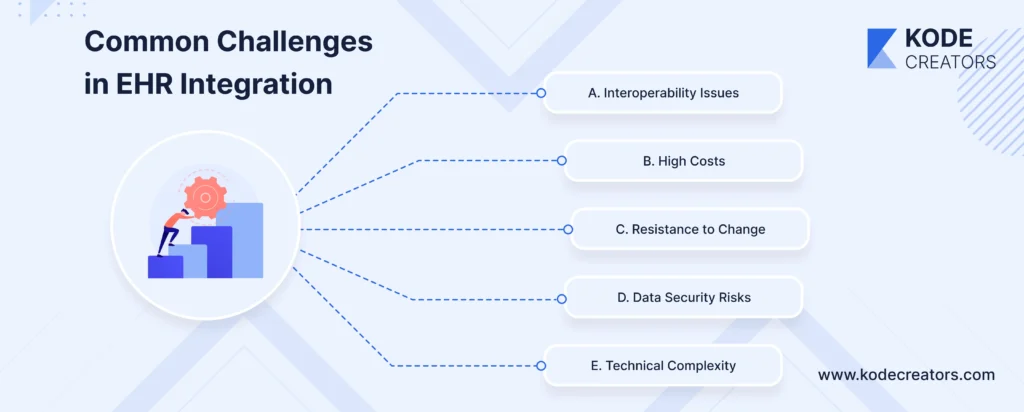
A. Interoperability Issues
Your new EHR speaks French. Your lab system speaks German. The billing software you have speaks ancient Greek. Welcome to healthcare IT, where nothing talks to anything else naturally.
The core problem? Lack of standardization. Every vendor builds their system differently, using proprietary formats that don't play nice with others. You end up with data stuck in silos, requiring manual transfers or expensive custom interfaces.
The Solution: APIs and FHIR standards are your universal translators. Push vendors to provide open APIs—no excuses. Adopt FHIR (Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources) as your standard. It's becoming the industry norm, and systems that don't support it are already obsolete. If a vendor says their system is "proprietary" and can't integrate, find another vendor.
B. High Costs
Sticker shock is real. Initial implementation runs $15,000-70,000 per provider. Then come the surprises: custom interfaces ($10,000 each), training ($5,000+), ongoing maintenance (15-20% of initial cost annually). Suddenly your $100,000 project is pushing $250,000.
The Strategy: Start with brutal budget honesty. Include everything: licenses, hardware, training, interfaces, maintenance, and a 20% contingency fund for surprises. Run an ROI analysis—factor in reduced transcription costs, fewer denied claims, increased patient volume. Most practices break even within 18-24 months if they plan properly. Get everything in writing. "Hidden" costs aren't hidden if you ask the right questions upfront.
C. Resistance to Change
"The old system worked fine." "This is too complicated." "I don't have time to learn this." Sound familiar? Clinicians and staff didn't sign up to be IT guinea pigs. They're already overwhelmed, and you're asking them to relearn everything.
The Solution: Change management isn't optional—it's critical. Start communication early. Explain why you're integrating (better patient care, less paperwork) not just what's changing. Identify champions in each department—respected staff who can influence others. Provide paid training time. Create super-users who become go-to helpers. Most importantly, listen to concerns and address them. Resistance often masks legitimate workflow issues.
D. Data Security Risks
Migration is when you're most vulnerable. Data moving between systems, temporary access permissions, multiple vendors touching sensitive information—hackers love integration projects. One breach during migration averaged $4.88 million in healthcare last year.
The Solution: Encryption everywhere—data at rest, in transit, in backups. Implement strict access controls with audit logs showing who touched what and when. Run security assessments before, during, and after migration. Use secure file transfer protocols, never email or USB drives. Test disaster recovery plans. Paranoid? Good. That paranoia prevents headlines about your data breach.
E. Technical Complexity
That legacy system from 2008 running on Windows Server 2003? Yeah, it needs to integrate too. Legacy systems weren't built for modern integration. They lack APIs, use outdated databases, and their original developers probably retired.
The Solution: Partner with IT vendors who've seen it all. They know workarounds, have pre-built interfaces, and won't be surprised when your old system throws weird errors. Sometimes middleware or interface engines can bridge the gap. Sometimes you need creative solutions like robotic process automation. The key? Don't try to figure this out yourself. Experience matters here
4. The Role of Emerging Technologies in EHR Integration
EHR integration isn't just about connecting what you have—it's about preparing for what's coming. The healthcare tech explosion is happening now, and your integrated system needs to handle it.

AI and Machine Learning: Your New Digital Assistant
AI is killing the most hated part of healthcare—data entry. Natural language processing transcribes doctor-patient conversations directly into structured EHR fields. No more typing while trying to maintain eye contact. Machine learning algorithms spot patterns humans miss—flagging potential drug interactions, predicting readmission risks, identifying patients likely to skip appointments.
One hospital using AI-powered EHR integration cut documentation time by 45% and caught 23% more potential adverse drug events. The AI doesn't replace clinical judgment—it amplifies it by handling the grunt work and surfacing critical insights.
Cloud Computing: Scale Without the Headache
Forget buying servers that'll be obsolete in three years. Cloud-based EHR integration scales instantly. Adding 10 new providers? Click a button. Opening a satellite clinic? They're connected immediately. Need to access records during a power outage? The cloud doesn't care about your local weather.
The real game-changer is accessibility. Doctors review patient charts from home. Specialists access records during emergencies from any device. Rural clinics get enterprise-level capabilities without enterprise budgets. Cloud computing makes geography irrelevant—your EHR is wherever you need it.
IoT: Real-Time Data That Actually Matters
Patients are walking around with medical devices that generate thousands of data points daily. Continuous glucose monitors, smart blood pressure cuffs, Apple Watches detecting irregular heartbeats—all producing valuable health data that usually goes nowhere.
IoT integration changes that. Real-time data flows directly into EHRs. Doctors see glucose trends, not just spot checks. Cardiac patients get interventions before emergencies happen. Remote monitoring becomes actual monitoring, not periodic check-ins.
The providers thriving tomorrow are building integration architectures today that welcome these technologies, not fight them.
Conclusion
EHR integration isn't optional anymore—it's the foundation of modern healthcare delivery. We've covered the essentials: conducting proper needs assessments, choosing interoperable systems, and protecting data throughout the process. Yes, you'll face challenges—interoperability headaches, cost overruns, staff resistance, and legacy system nightmares. But with the right approach (APIs, FHIR standards, change management, and experienced partners), these obstacles become manageable speed bumps, not roadblocks.
The future of healthcare is connected, automated, and intelligent. AI will handle documentation as doctors focus on patients. Cloud platforms will make location irrelevant. IoT devices will stream real-time health data directly into patient records. The providers who build robust integration frameworks today will thrive in this connected ecosystem. Those who don't will struggle with disconnected systems while competitors deliver seamless care.