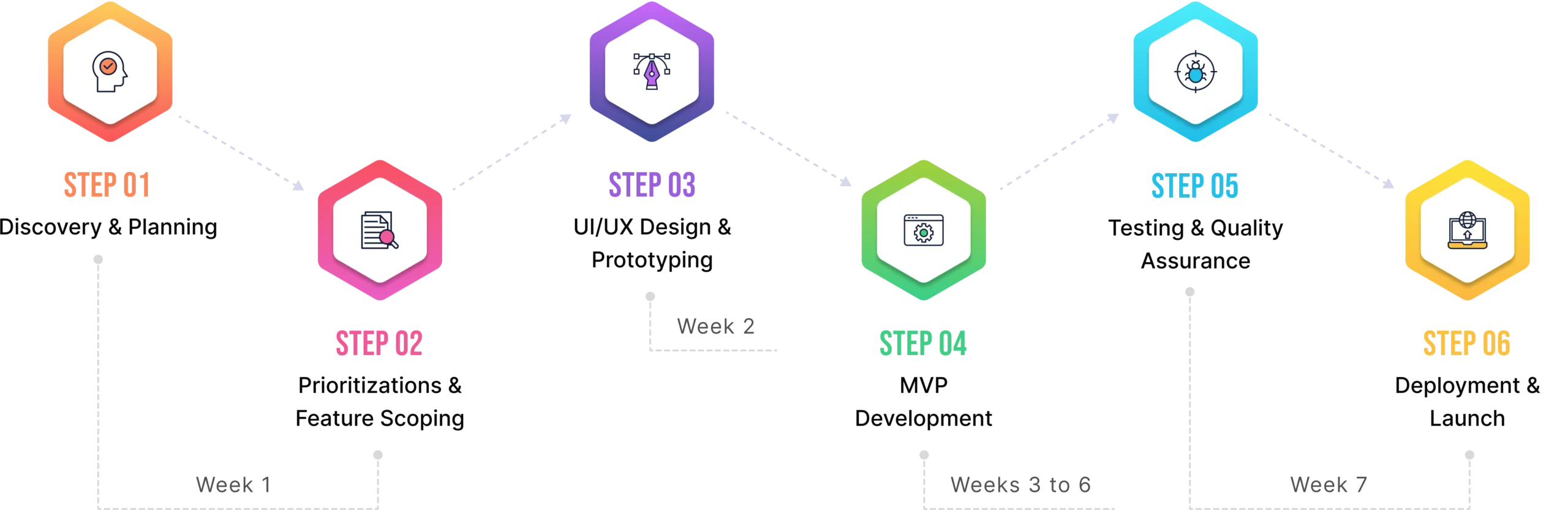
An idea is the starting point for every great app, but not every idea becomes a great app. Even the most promising concepts without proper validation can fall short wasting time, money, and effort. Validation is your safety net that guarantees your app idea is a real thing that people need and are ready to pay for. It’s a systematic process to see if your concept is worth pursuing before you dive into development.
42% of startups fail due to a lack of market need for their product, so validating an idea is important before diving into development. Thorough validation became all the more important after this startling statistic. A product that has genuine demand won’t have to overcome a lot of challenges; therefore, it's best to identify the problems you need to solve and who needs them addressed early on. The process of validating an app is not just another step, it's the first step to making that app a success.
The Cost of Skipping Validation
Skipping validation has led to the downfall of many promising apps. For instance, Quibi, a short-form video streaming platform, raised over $1.75 billion but shut down within six months. One of its critical failures was assuming a demand for premium, mobile-specific content without validating user interest. This oversight resulted in massive financial losses and a tarnished brand reputation.
Additionally, data shows that 90% of apps are uninstalled within a month of download, often because they fail to meet user expectations or address genuine pain points. Research from Exploding Topics reveals that 10% of startups fail within the first year, emphasizing the risks of building without understanding your audience.
Investing in validation upfront is not just about risk management—it’s about maximizing returns. When you uncover user preferences and market demands early, you can channel resources into building features and experiences that truly matter. Validation ensures that your app development is rooted in facts rather than assumptions, paving the way for long-term success in a crowded and competitive digital space.

How to Validate Your App Idea: 8 Simple Steps
Your app idea is great. Perhaps, it's one in a million! But does it solve a problem? Do you think there is a market need for it? Here are 8 eight simple steps that will help you validate your app idea.
Step 1: Identify the Core Problem
The foundation of any successful app lies in addressing a genuine problem. Begin by asking, What specific issue does my app aim to solve? Clearly defining this core problem not only sharpens your vision but also resonates with potential users who share the same pain points. For example, Slack redefined team communication by solving the fragmented messaging and workflow challenges faced by modern workplaces.
Tools like problem statements help crystallize your app’s purpose. A problem statement should clearly articulate the issue, its impact, and who it affects. For instance: “Small businesses struggle with expense tracking due to complex software, leading to wasted time and errors.”
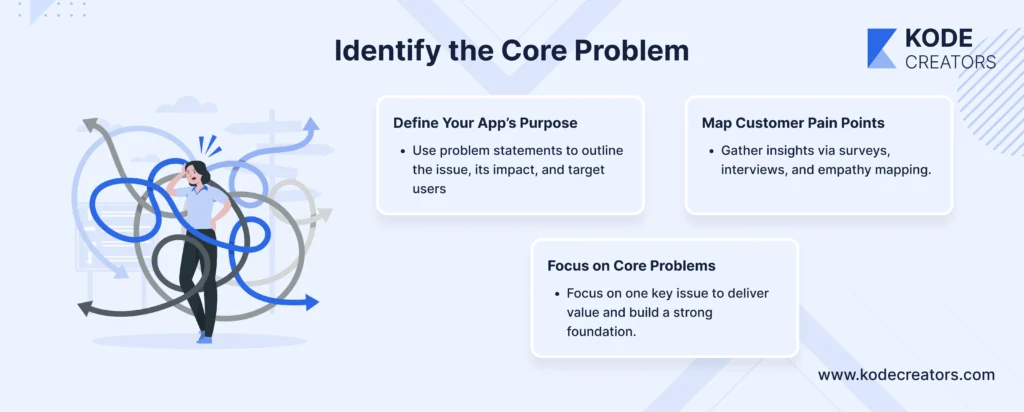
Customer pain point mapping is another powerful tool. Engage with your target audience via surveys, interviews, or social listening to identify frustrations or unmet needs. Use methods like empathy mapping to explore users' feelings, goals, and challenges. This approach ensures you’re not making assumptions but building a solution grounded in real-world data.
When you focus on solving one core problem effectively, your app can stand out and provide meaningful value, setting a strong foundation for further development.
Step 2: Conduct Market Research
Market research is essential for validating your app idea and identifying opportunities within your niche. Start by analyzing the industry landscape to understand current trends, potential competitors, and untapped gaps. A successful app idea isn’t just about solving a problem—it’s about ensuring there’s demand for the solution.
Competitor Analysis
Identify direct and indirect competitors. Study their strengths, weaknesses, user reviews, and app store ratings. Tools like App Annie and SimilarWeb can provide valuable insights into competitor performance and user engagement. For example, analyzing reviews on competitors’ apps often reveals gaps, like missing features or customer dissatisfaction, that your app can address.

Target Audience Insights
Understanding your audience’s needs is equally crucial. Use tools like Google Trends, Statista, or social media analytics to gauge interest in your app’s core idea. Conduct surveys or focus groups to hear firsthand from potential users about their preferences, pain points, and expectations.
Data-Driven Validation
Support your findings with statistics. For example, if you’re building an e-commerce app, note how mobile shopping trends are growing rapidly, with mobile commerce projected to reach $710.4 billion by 2025. This kind of data not only validates your idea but can also guide development priorities.
Thorough market research ensures you’re not entering the field blindly. It lays the groundwork for a well-informed, user-centric app development process.
Step 3: Validate the Target Audience
Understanding your target audience is crucial to ensure your app meets their specific needs. Begin by creating detailed user personas—fictional representations of your ideal users. These personas should include demographics like age, location, income, and education, as well as psychographics such as goals, pain points, and digital habits. For example, if your app is a fitness tracker, your primary persona might be a 25–35-year-old working professional seeking efficient workout solutions due to a busy schedule.
Gathering Insights
Engage directly with your target audience to validate your assumptions. Use methods like:
- Surveys: Tools like Google Forms or SurveyMonkey can help collect responses at scale. Ask about their current challenges and preferred app features.
- Interviews: Conduct one-on-one conversations to dive deeper into user needs.
- Focus Groups: Gather small groups to discuss your app concept and get diverse perspectives in real-time.
Analyze Behavioral Data
Supplement qualitative research with behavioral insights. Social media platforms and analytics tools can help uncover trends and interests relevant to your audience. For instance, if your target group is active on Instagram, this might influence your app’s design or marketing strategies.
Validating your audience through real-world feedback and data makes sure your app addresses genuine needs and paves the way for higher engagement and adoption.
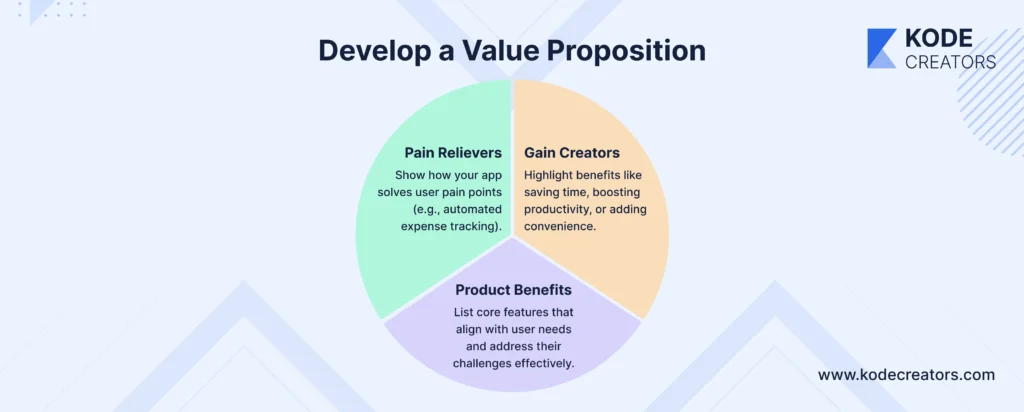
Step 4: Develop a Value Proposition
Your value proposition is the cornerstone of your app’s success. It clearly articulates how your app solves users’ problems and delivers unique benefits. To build a compelling value proposition, create a Value Map, which outlines three key components:
- Pain Relievers: Identify how your app addresses specific user pain points. For example, if users struggle with managing expenses, your app could provide features like automated categorization of transactions or personalized budgeting tips.
- Gain Creators: Highlight the positive outcomes your app enables. This could include saving time, improving productivity, or enhancing convenience. For instance, a fitness app might offer AI-driven workout plans tailored to individual goals.
- Product Benefits: List the core features of your app that support these gains and alleviate pains. This ensures your app’s functionality aligns with user expectations.
Tie it to User Challenges
A strong value proposition directly connects these elements to real-world challenges. For example, a language-learning app might focus on users’ struggles with time constraints and emphasize its “10-minute micro-lessons” feature as a solution.
Example Framework
Use the “XYZ” model to refine your messaging:
- We help [target audience]
- Solve [specific problem]
- By providing [unique solution]
This structured approach ensures your app's benefits resonate with users, driving engagement and retention.
Step 5: Create a Prototype or Wireframe
Creating a prototype or wireframe is a critical step in app validation. These visual representations help simulate user interaction and bring your idea to life, allowing stakeholders and potential users to understand its functionality without full development.
Tools for Prototyping
- Figma and Adobe XD: These platforms allow you to create high-fidelity designs with interactive elements to mimic app navigation.
- Balsamiq: Ideal for low-fidelity wireframes, focusing on structure rather than design.
- InVision: Enables linking wireframes to create clickable prototypes, ideal for usability testing.
Prototyping helps identify gaps in your design and functionality early on, saving significant resources. For example, a food delivery app prototype might reveal user confusion about placing an order, prompting design adjustments.

Usability Testing
Once the prototype is ready, conduct usability testing to gather insights:
- A/B Testing: Compare two versions of a feature or layout to identify the more effective option.
- User Testing: Share the prototype with a sample group from your target audience to observe their interactions. Tools like UsabilityHub can facilitate this process.
These iterative tests allow you to refine your app idea, ensuring the final product aligns with user expectations and preferences. Keep this in mind: when you invest time in prototyping, you reduce the risk of launching an app with design or functionality flaws.
Step 6: Test the Idea with a Minimum Viable Product (MVP)
Launching a Minimum Viable Product (MVP) is a proven way to validate your app idea. Releasing a lean version with core functionalities will help you gain invaluable insights while minimizing investment and risk.
Why does an MVP Matter?
An MVP focuses on delivering essential features that solve the primary problem for your target audience. This approach helps you:
- Save Resources: Avoid the costs of developing unnecessary features.
- Gauge Market Interest: Assess if your app resonates with users before scaling.
- Collect Feedback: Understand what users value most and what needs improvement.
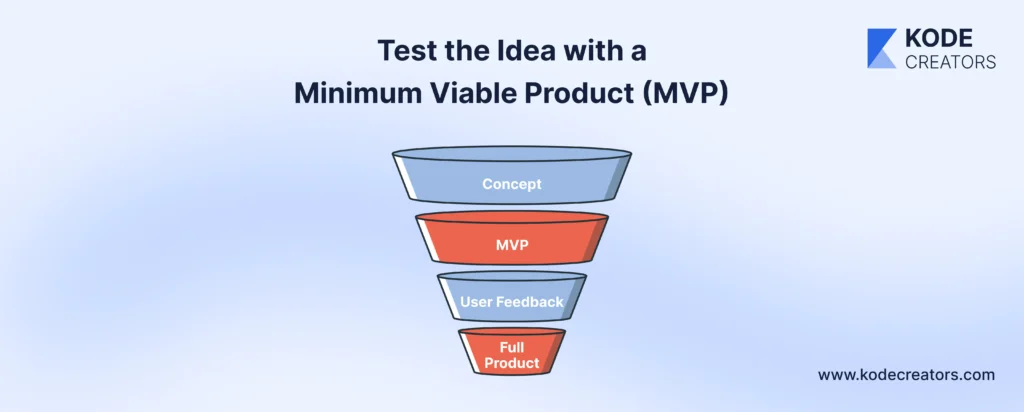
Gathering User Feedback
Once your MVP is live, actively collect feedback through:
- Surveys and Reviews: Ask users about their experience, highlighting pain points or desired features.
- Analytics Tools: Platforms like Mixpanel or Google Analytics track user behavior, revealing what works and what doesn’t.
For instance, Dropbox initially launched as an MVP in the form of an explainer video showcasing its core features. This simple strategy validated user interest, with thousands signing up for the service before full-scale development.
Iterate Based on Feedback
The goal of an MVP is iteration. Use the data and feedback to refine your app, adding or modifying features to better meet user needs. This cycle of building, testing, and learning ensures your app evolves in alignment with market demands, significantly improving its chances of success.
Step 7: Use Analytics and Feedback
Harnessing analytics and feedback is crucial for validating your app’s features and refining its development process. By systematically tracking user behavior and analyzing responses, you can make informed decisions about what works and what needs improvement.
Implementing User Behavior Tracking
Analytics tools like Google Analytics for Firebase or Mixpanel help monitor user interactions, revealing patterns such as:
- Feature Usage: Identify which features are most and least utilized.
- Drop-Off Points: Understand where users abandon the app, which could indicate confusion or dissatisfaction.
- Engagement Metrics: Measure user retention, session duration, and conversion rates to assess overall satisfaction.
For instance, if users frequently skip a registration step, it might be too complex or unnecessary for early engagement.

Analyzing Feedback for Risks and Opportunities
User feedback provides a qualitative complement to analytics. Collect data through:
- Surveys and Reviews: Direct questions can reveal frustrations or missing functionalities.
- In-App Feedback Forms: Allow users to share suggestions while using the app.
For example, Slack relied heavily on beta user feedback to fine-tune its messaging features, leading to the intuitive interface loved by millions today.
Turning Insights into Action
Combine quantitative analytics with qualitative feedback to:
- Address Pain Points: Fix issues that hinder the user experience.
- Uncover Opportunities: Identify new features or enhancements users are willing to pay for.
This iterative process ensures your app evolves in line with real-world needs, reducing risks and maximizing its market potential.
Step 8: Address Monetization Strategy
A strong monetization strategy is pivotal for your app’s long-term success. Addressing how your app generates revenue during the validation stage ensures its financial viability and aligns with user expectations.
Testing Revenue Models
Different apps thrive on diverse revenue models, including:
- Subscriptions: Popular among streaming services and fitness apps, offering steady income through recurring payments.
- In-App Purchases: Gaming apps often leverage this model, allowing users to buy add-ons or premium features.
- Freemium: Provides free basic features with premium upgrades, commonly used by productivity apps like Trello.
- Advertising: Effective for apps with high user engagement, though it risks alienating users if overused.
Use A/B testing to experiment with these models. For instance, test two pricing tiers for subscriptions or different ad placements to see which generates better results without compromising the user experience.
Evaluating Financial Viability
Analyze the feedback and behavior of early adopters to gauge willingness to pay. Ask these questions:
- Are users converting from free to paid features?
- Do they find the pricing reasonable compared to the value offered?
- Does the chosen model align with app usage patterns?
Real-Life Example
When Spotify introduced its freemium model, it tested how many users would upgrade to premium plans and adjusted its offering based on user behavior. This strategy helped it achieve over 200 million paid subscribers worldwide.
Early monetization makes sure the app solves user problems and becomes profitable.
Common Mistakes to Avoid During Validation
1. Skipping Thorough Research
One of the biggest pitfalls in app validation is insufficient market research or relying solely on surface-level assumptions. Entrepreneurs often fall into the trap of confirmation bias—seeking data that supports their idea rather than uncovering potential challenges. A lack of comprehensive research into competitor strategies, target audience needs, or market trends can lead to developing an app that doesn’t resonate with users.
2. Biased Feedback Loops
Feedback collected from friends, family, or overly loyal early adopters may skew the validation process. This kind of biased feedback often gives a false sense of approval. Instead, ensure that feedback comes from a representative sample of the target audience, as they are more likely to provide constructive criticism and honest insights.
3. Ignoring Monetization Testing
Neglecting to test potential revenue streams is another frequent oversight. For example, failing to validate whether users are willing to pay for premium features or subscriptions can lead to significant financial risks. Conducting A/B tests on pricing tiers or revenue models ensures that the monetization strategy aligns with user expectations.
4. Underestimating Scalability Issues
Some app ideas may seem viable initially but fail to scale efficiently as user demand grows. Overlooking scalability during the validation stage can lead to technical debt and operational bottlenecks once the app gains traction.
Pro Tip
To avoid these mistakes, ensure the validation process is data-driven, iterative, and unbiased. By prioritizing thorough research, unbiased feedback, and scalable strategies, you lay the groundwork for a successful app launch.
Conclusion:
Validating your app idea is not just a preliminary step but a cornerstone of its success. From identifying the core problem to testing a monetization strategy, each step builds a strong foundation to ensure your app meets real user needs and market demand. When you approach validation with thorough research, unbiased feedback, and iterative improvements, you reduce risks, save resources, and set your project up for sustainable growth. Before diving into full-scale development, use insights from the validation process to refine and optimize your concept, ensuring it’s not just an idea but a solution poised for success.